What is SSL & TLS?
What is Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) and Transport Layer Security (TLS)? Both SSL and TLS are protocols those are responsible of making a secure internet connection between two different systems. This secure data transferring prevents any criminals from reading or editing the data that is getting transferred between the two systems. The difference between both SSL and TLS is basically when they first came out. TLS is known as SSL’s successor, meaning it’s an upgraded version of SSL.

Try it yourself
You can easily indicate if SSL/TLS is being used in a website. Simply check the top side of your browser and look for the website’s URL address. If the URL address starts with “https”, then the website has been confirmed or verified to be secure. However, if the URL address starts with “http”, it means the website has not yet been confirmed or verified to be secure.
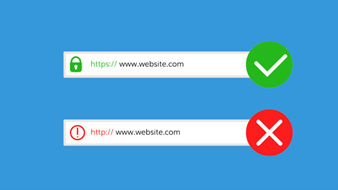
There are also visual indicators in browsers to determine if your website is secure or not. Simply find for the lock icon next to the website’s URL address. Most web browsers have their visual indicators located on the left-hand side of where the URL address is located. Others are mostly located on the right-hand side of where the URL address is located. When the lock icon is not shown and something else or nothing is shown, it means the website is not secure.
HTTP vs HTTPS
After reading the paragraph above, you may wonder if all http is insecure. The answer is no. Let’s go over this in detail.
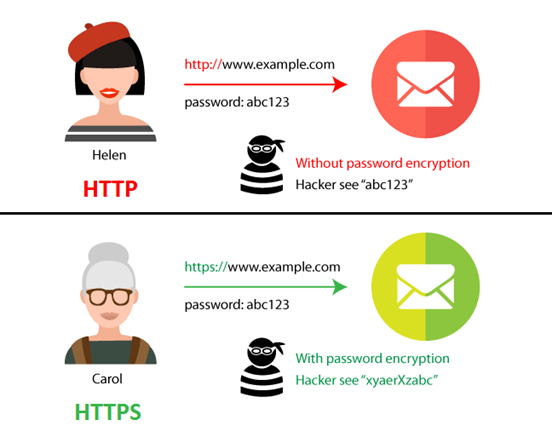
The main purpose of Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) is showing the client a functioning website. You can interact with the website, navigate around several pages and you will not have any issues. However, the HTTP website is not meant for any secure data transfers between the client and the server. As an example, if you are entering your personal information to login into a HTTP website, there is a possibility where a cybercriminal may interact with your inputted data during its transfer to the server. This type of cyberattack is well known to cybersecurity specialists as, Man-In-The-Middle Attack.
To prevent this issue, Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure (HTTPS) was invented. HTTPS does the exact same job as HTTP, but HTTPS uses SSL to encrypt its information for secure data transferring between the client and server. Here’s an example; Most of the websites you visit, that is needing any type of your personal information is using HTTPS instead of HTTP.